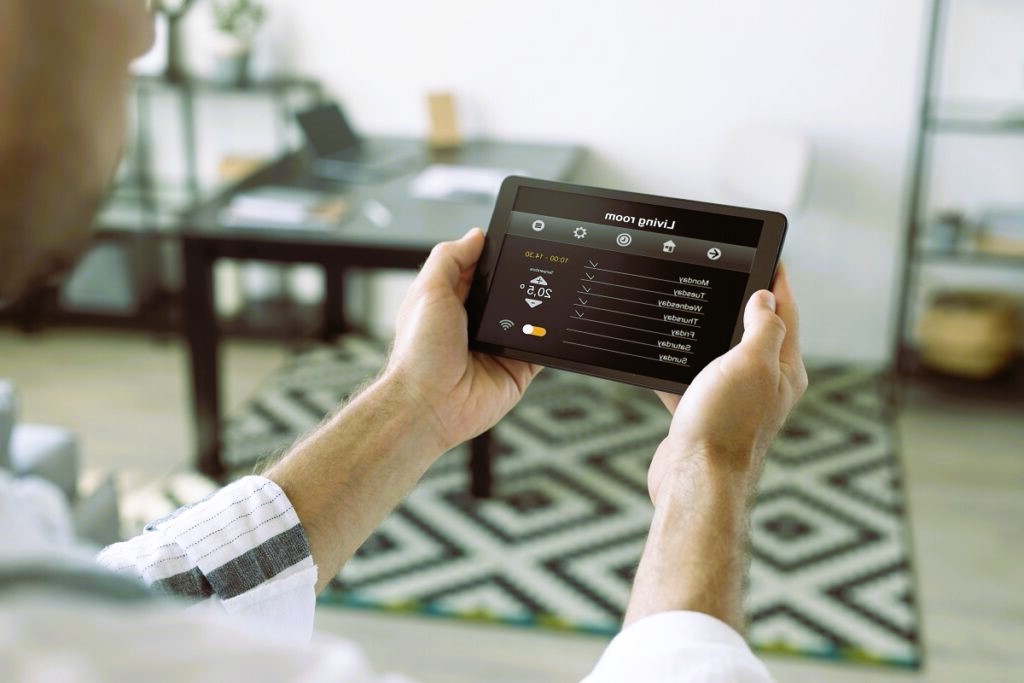
In the ever-evolving realm of smart homes, sensors play a pivotal role in transforming traditional houses into intelligent, responsive living spaces. These devices, capable of detecting and measuring various physical properties, contribute to the efficiency, security, and convenience of modern homes. Let’s delve into the diverse world of sensors designed for smart homes and explore the impact they have on our daily lives.
1. Introduction to Smart Home Sensors
Smart home sensors are devices that collect data from the environment and transmit it to a central hub or controller. This data is then processed to trigger specific actions, automate routines, or provide real-time insights. The types of sensors available for smart homes are expansive, catering to a wide range of needs and preferences.
2. Motion Sensors: Enhancing Security and Convenience
Motion sensors, also known as occupancy sensors, are commonly employed for both security and convenience purposes. These sensors detect movement within a designated area and can be integrated with lighting, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC), and security systems. By automatically turning on lights or adjusting climate settings when motion is detected, these sensors contribute to energy efficiency and enhance security.
3. Door and Window Sensors: Fortifying Security
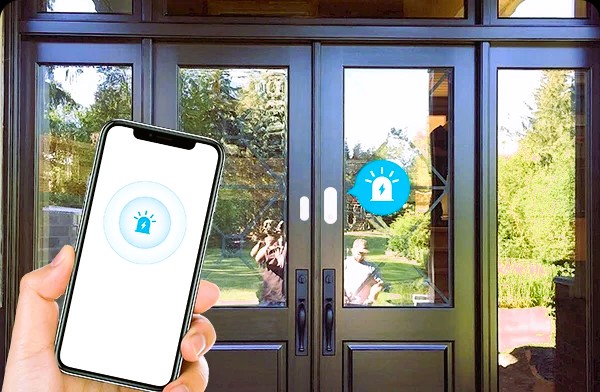
Door and window sensors are fundamental components of smart home security systems. Consisting of two parts—one attached to the door or window and the other to the frame—they trigger an alarm or notification when the connection is broken, indicating unauthorized entry. Integration with smart home platforms allows users to receive alerts and monitor the status of doors and windows remotely.
4. Temperature and Humidity Sensors: Climate Control Precision
Temperature and humidity sensors enable precise climate control within a smart home. Integrated with heating and cooling systems, these sensors ensure optimal comfort while maximizing energy efficiency. Users can remotely monitor and adjust temperature and humidity levels, creating a personalized and efficient home environment.
5. Light Sensors: Adaptive Illumination
Light sensors, or ambient light sensors, measure the intensity of light in a space. This information is utilized to adjust artificial lighting accordingly, optimizing energy consumption. In smart homes, light sensors contribute to energy efficiency by automatically dimming or brightening lights based on natural light conditions.
6. Smoke and Gas Sensors: Early Warning Systems
Smoke and gas sensors are integral for ensuring the safety of residents. These sensors detect the presence of smoke, carbon monoxide, or other harmful gases, triggering alarms and notifications in case of an emergency. Early detection provided by smart sensors can be crucial in preventing potential hazards. Read about the main components of creating a smart home.
7. Water Leak Sensors: Preventing Property Damage
Water leak sensors serve as guardians against water-related disasters. Placed in areas prone to leaks or flooding, these sensors detect the presence of water and send alerts to homeowners. Quick response to potential leaks helps prevent property damage and mold growth.
8. Smart Cameras: Visual Intelligence
While often considered as part of security systems, smart cameras equipped with advanced sensors deserve a mention. These devices offer visual intelligence, with features such as facial recognition, motion tracking, and live streaming. Integrated with other sensors, smart cameras provide comprehensive security solutions.
9. Integrating Sensors for a Seamless Experience

The true power of smart homes lies in the seamless integration of various sensors. Centralized control hubs, such as those compatible with ISO standards, facilitate communication and coordination among different devices. This interoperability allows users to create personalized automation scenarios, ensuring that actions triggered by one sensor can influence the behavior of others.
10. ISO Standards: Ensuring Interoperability and Quality
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) plays a vital role in establishing standards that contribute to the interoperability and quality of smart home technologies. ISO standards cover a broad spectrum, including communication protocols, security measures, and testing methodologies. These standards ensure that devices from different manufacturers can work together seamlessly, fostering a more open and competitive market.
For more detailed information on ISO standards related to smart home technologies, visit the official ISO website here.
11. The Future of Smart Home Sensors
As technology continues to advance, the landscape of smart home sensors will evolve. Emerging technologies such as edge computing, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) will likely contribute to more intelligent and responsive sensor networks. From health monitoring to predictive maintenance, the possibilities for sensor applications in smart homes are vast.
In conclusion, smart home sensors are the unsung heroes of modern living, enhancing our homes in ways that were once unimaginable. The journey towards a fully integrated and intelligent home begins with understanding the capabilities of these sensors and embracing the standards that ensure their effectiveness. As we move forward, the synergy between innovative sensor technologies and standardized practices will shape the future of smart homes.